Europa Universalis V Trade Guide: Mastering Dynamic Markets & Trade Networks
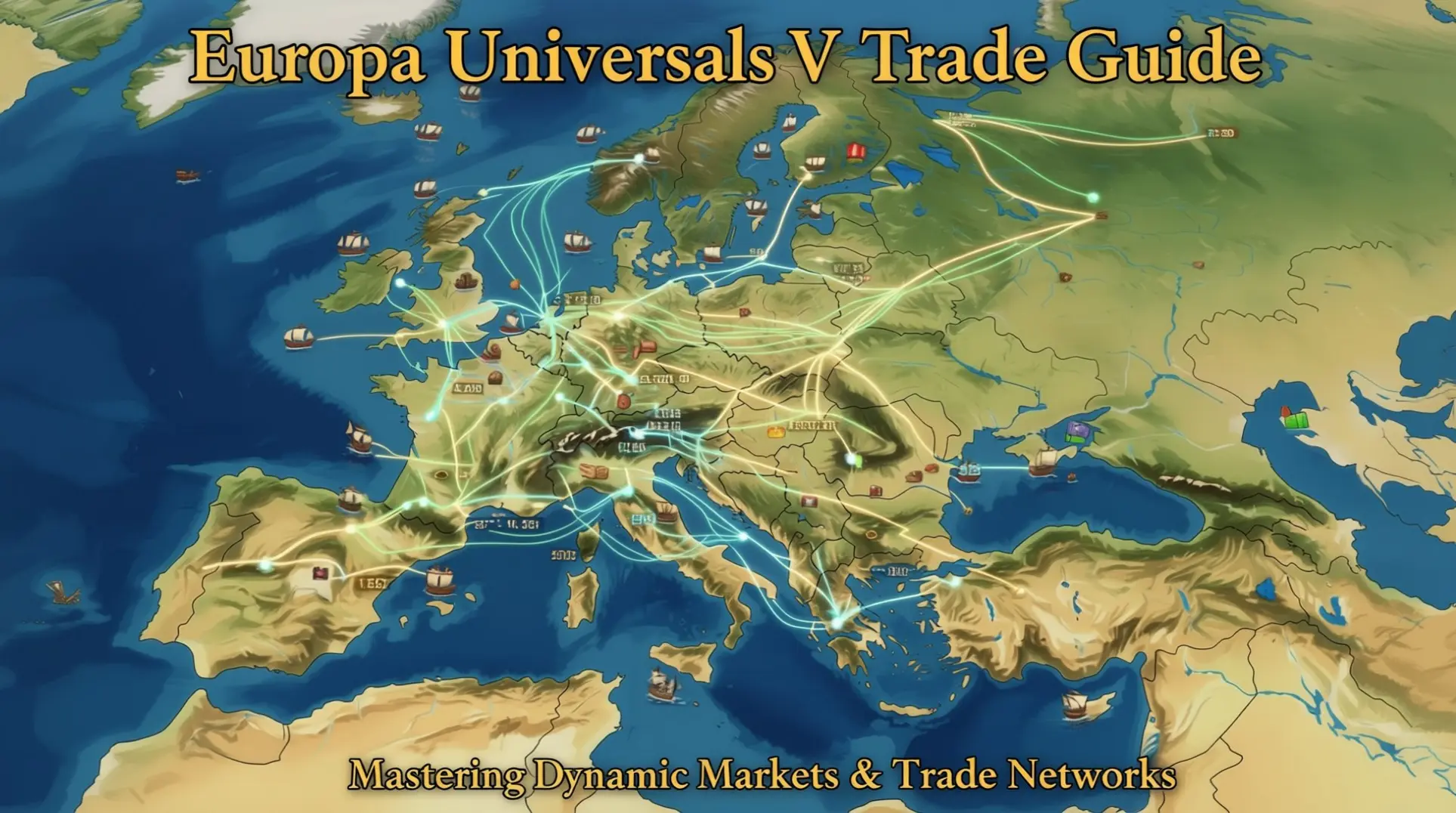
The Foundation: Dynamic Markets vs. Static Nodes
What Are Dynamic Markets?
Dynamic markets in Europa Universalis V are not fixed, static trade nodes. They evolve constantly based on player actions and global conditions, creating a moving and adaptive trade network. The dynamic market system underpins a broad network of production chains across more than 70 unique goods. All these goods feed into evolving market demand and supply.
Market Center: The heart of a market through which all trade routes and economic activity flow. Control over a Market Center determines where goods flow. Markets can expand to include new provinces or retract, effectively reshaping which territories participate. This dynamism is driven by key variables including Market Attraction, Market Protectionism, and Distance between provinces and a Market Center.
Trade Capacity and Market Access: These govern a nation's ability to participate in trade and connect its provinces to markets.
Trade Advantage: This becomes the deciding factor when multiple nations compete to export the same good in a profitable market. Higher Trade Advantage increases your goods' priority.
Players can create or destroy Market Centers, fundamentally reshaping the trade map by altering where trade originates and concentrates. Owning and strategically leveraging Market Centers is essential to directing the flow of wealth and gaining economic dominance.
Key Differences from EU4 Trade Nodes
- Fixed vs. Dynamic: EU4 uses fixed trade nodes with predetermined routes. EU5 uses dynamic markets that expand, contract, and relocate based on market attraction and economic factors.
- Abstract Value vs. Actual Goods: EU4 represents trade by abstract 'trade value' moving between nodes rather than tracking specific goods. EU5 models the actual movement of around 70 unique goods feeding evolving demand and supply.
- Market Centers: The Market Center is the central hub through which all trade routes and economic activity flow in EU5. Players can create or destroy Market Centers, reshaping the trade map by changing where goods originate and concentrate.
- Trade Controls: EU5 introduces Trade Capacity and Market Access as key controls on how a nation participates in each market.
- Automation: Trade in EU5 can be automated, with a system handling day-to-day buying and selling so players can focus on diplomacy and expansion.
Core Trade Mechanics in EU5
Market Access: The Gateway to Prosperity
Market Access: A percentage measure of a location's ability to connect to a market and engage in trade. If a province has low or zero Market Access, it cannot effectively buy or sell the goods it produces, leading to shortages and lost profits.
Market Access is visible in the UI when hovering over a market, showing surplus/needs and the access level for your locations. Geographic proximity and control of connecting trade routes are the primary determinants of Market Access. Market Attraction and Market Protection modulate access by boosting or restricting it. Trade Capacity infrastructure, such as ports and warehouses, influences Market Access by increasing throughput.
Poor Market Access can cause stagnating income as goods cannot reach profitable markets. It can also lead to goods shortages in provinces, reducing efficiency and tax income. Economic isolation can occur if a nation is cut off from major markets due to low Market Access or blocked routes. Strategies to improve Market Access include owning or establishing a Market Center, securing trade routes, investing in infrastructure, and using diplomacy to improve terms.
Trade Capacity: Managing Economic Flow
Trade Capacity: Represents your merchants' ability to move goods between markets, with each market having a specific amount that is consumed by both imports and exports. It acts as economic bandwidth: the more capacity you have, the more goods you can move and the greater your potential profits.
Infrastructure investments directly increase a market's trade capacity, with Marketplaces, Trade Offices, and Ports providing primary capacity boosts. Trade capacity is per market and is spent to import or export goods to and from that market. UI indicators show import routes as blue lines and export routes as orange lines when selecting a market, reflecting capacity usage.
The Market Center is the central hub through which all trade routes flow, and its efficiency is determined by supply, demand, and the available trade capacity. Players can create or destroy Market Centers to reshape the trade map by changing where goods originate and concentrate. Market Access interacts with capacity to determine overall trade potential; higher access plus more capacity expands trade reach. Trade profits are distributed among estates, including the Crown, according to their power, linking capacity to real economic returns.
Population-Driven Trade
Population in EU5 is composed of distinct 'pops' with specific economic roles: peasants (agriculture/food), laborers (raw materials), and burghers (trade and manufactured goods). Population growth is primarily driven by the food supply; a food surplus fuels growth while deficits hamper it.
Resource Gathering Operations (RGOs) are the main source of raw materials, with output tied to province infrastructure and the local population working there. Manufacturing and production buildings, often driven by the burgher class, convert raw materials into higher-value manufactured goods, boosting income. Consumption by the population creates demand; meeting these demands sustains prosperity and stabilizes tax revenue and production.
Trade Capacity and Market Access determine how effectively a nation can move goods and reach profitable markets; both are essential to trading activity. The Market Center acts as the central hub through which trade routes flow, and control over it shapes where goods originate and concentrate. Trade profits are distributed among estates, linking capacity and market access to real economic returns.
Building Your Trade Network
Early-Game Trade Strategy
In the early game, establish a single main market to concentrate capacity and make income easier to defend. Use short, protected trade routes to shield your initial income from rivals and ensure a stable early cash flow.
Trade Capacity: This is the amount of trade value you can move through a market and is a key limiter on early expansion. Infrastructure investments raise trade capacity, so look to marketplaces, trade offices, and ports for capacity boosts. Manual trade management can yield strategic gains, especially when targeting markets with early Institutions. Some guides highlight manual routing as a core EU5 skill to accelerate Institutions spread and improve long-term tech and economy.
Focus on expanding capacity and leveraging the Market Center to increase control over where goods originate and concentrate. Plan your spending by investing in infrastructure and trade buildings before pursuing high-immediate-profit options.
- Consolidate in one market for defensible income
- Use protected, short routes for stable cash flow
- Establish Trade Offices in foreign nations when relations are strong for additional capacity
Infrastructure Investment Priorities
Early-game priority is to invest first in Marketplaces and Wharfs in core provinces to rapidly boost domestic trade capacity and establish a solid base. This domestic focus should be consolidated before expanding outward with foreign Market Centers.
Marketplaces: These are a fundamental domestic investment that significantly raise trade capacity, enabling more goods to be moved and profit earned.
Wharfs: These ports are essential for boosting trade range and improving the efficiency of coastal trade routes. Ports should be upgraded along key trade routes to extend reach to distant markets and to import scarce goods for population needs.
Trade Offices: These are critical for projecting influence into foreign markets and extracting wealth from nodes you do not directly control. A well-developed infrastructure network, supported by trade offices and ports, enables faster expansion and greater long-term trade profits.
A synergistic approach—placing Marketplaces, Ports, and Wharfs in the same province—creates a powerful trade hub and a multiplier effect on income. Plan infrastructure spend to outpace immediate-profit options, as prioritizing long-term capacity yields bigger returns as markets grow.
- Invest in Marketplaces and Wharfs in core provinces first
- Upgrade ports along key trade routes to extend market reach
- Create synergistic hubs by stacking buildings in the same province
Advanced Trade Strategies
Competing for Market Dominance
Market Centers are the heart of any market. All trade routes and economic activity flow through these hubs, and controlling one determines where goods concentrate and originate.
Trade Advantage: This becomes the deciding factor when multiple nations compete to export the same good in a profitable market. Higher Trade Advantage increases your goods' priority over rivals.
Owning a Market Center grants powerful bonuses including +2 Trade Capacity, +20 Trade Advantage, and +0.025 Migration Attraction. The owner can also embargo rivals using the same market, giving them a powerful tool to control market access.
Market Access: Geographic proximity and control of connecting trade routes are the primary determinants of access. Market Attraction and Market Protection can boost or restrict this access. Early-game strategy should emphasize consolidating in one market while using protected routes. Gradually increase your trade capacity to ensure long-term growth and economic dominance.
- Create or destroy Market Centers to fundamentally reshape the trade map
- Use Trade Offices to project influence into foreign markets and extract wealth from nodes you don't directly control
- Place Marketplaces, Ports, and Wharfs in the same province to create a powerful trade hub with a multiplier effect on income
Responding to Market Dynamics
EU5 markets are dynamic, living systems that expand or retract based on Market Attraction and Market Protectionism. These systems evolve through over 70 unique goods with shifting demand and supply.
Trade Capacity: This is the amount of trade value you can move through a market, consumed by both imports and exports. Infrastructure investments raise this capacity, with marketplaces, trade offices, and ports providing primary boosts.
Market Access works together with Capacity to determine how effectively your nation connects provinces to markets and how far trade can reach. To adapt to changing conditions, focus on expanding Market Attraction, securing trade routes, and investing in infrastructure. Population mechanics are deeply intertwined with trade. Population growth is driven by food supply and demand, which influences labor, production, and tax revenues.
- Use embargoes as a strategic tool to disrupt rivals if you own a Market Center
- Create or destroy Market Centers to reshape where goods originate and concentrate
- Monitor wars, blockades, and other nations' policies that can disrupt established trade routes
Automation vs. Manual Control
When to Use Automation
Automation delivers efficiency, stability, and reduced micromanagement. It's perfect for beginners learning the ropes and essential for managing sprawling empires in mid to late game. Let automation handle routine market operations and trade decisions. This delegation frees you to focus on military campaigns, diplomacy, and strategic expansion.
- Best for beginners overwhelmed by complex manual management
- Essential for large empires during mid to late game expansion
- Manages the bulk of routine trade operations
- Allows focus on diplomacy, military campaigns, and expansion
Manual Optimization Techniques
Manual control is indispensable for precision, maximizing profits, and executing advanced economic warfare. It empowers you to spot and exploit lucrative opportunities that automation overlooks. Manual trading shines with strategic goals like importing shortage materials, orchestrating embargos, and long-term market manipulation. Advanced players use it to target early Institution markets, accelerate their spread, and focus on high-demand goods.
- Import crucial shortage materials strategically
- Orchestrate trade embargos to cripple rival economies
- Create artificial shortages in enemy markets or flood markets to drive down prices
- Target markets with early Institutions to accelerate spread and improve tech
- Focus trade on specific goods that are strategically important
- Execute precise, high-impact economic strategies
Patch 1.0.8 Trade Updates
New Trade Range Map Mode
Patch 1.0.8 introduces a new Trade Range Map Mode: A visual tool that helps players assess trade influence and reach across markets. The update significantly reduces trade-related scaling costs. This aims to provide greater flexibility for trade-focused economies. These changes are part of a broader economic rebalance. The patch also includes over 300 bug fixes and new features addressing balance and UI issues.
- Players can test these changes in open beta by switching to the beta branch on Steam.
Decentralization Buffs
Patch 1.0.8 significantly buffs Decentralization: A governance approach for large empires with multiple power centers, making it a more potent and viable option. The update reverses the previous 'always centralization' modifier to an Always Decentralization Modifier: The new core governance dynamic that shifts how large realms operate.
These changes empower multi-vassal empires like France and Poland-Lithuania as viable strategies. Community reactions are mixed, with praise for flexibility but concerns about balance issues requiring hotfixes.
- Players can test decentralization changes in the open beta branch on Steam.
- These buffs are tied into broader economic and trade balance changes.
Common Trade Mistakes to Avoid
Overlooking Market Access
Market Access: This determines a province's ability to effectively buy or sell goods. If a province has low or zero Market Access, it cannot effectively buy or sell the goods it produces, leading to shortages and lost profits.
Poor Market Access can cause stagnating income as goods cannot reach profitable markets. Poor Market Access can lead to goods shortages in provinces, reducing efficiency and tax income. Economic Isolation: This occurs when a nation is cut off from major markets due to low Market Access or blocked routes.
Strategies to improve Market Access include:
- Owning or establishing a Market Center
- Securing trade routes
- Investing in infrastructure
- Using diplomacy to improve terms
Ignoring Population Dynamics
Population Growth: This is primarily driven by the food supply. A food surplus fuels growth while deficits hamper it. Consumption by the population creates demand. Meeting these demands sustains prosperity and stabilizes tax revenue and production.
Resource Gathering Operations (RGOs): These are the main source of raw materials, with output tied to province infrastructure and the local population working there. Manufacturing and production buildings, often driven by the burgher class, convert raw materials into higher-value manufactured goods, boosting income.
Population in EU5 is composed of distinct 'pops' with specific economic roles:
- Peasants (agriculture/food)
- Laborers (raw materials)
- Burghers (trade and manufactured goods)
Conclusion
Europa Universalis V's trade system represents a significant evolution from its predecessor, replacing static trade nodes with dynamic markets that respond to player actions and global economic conditions. The key to success lies in understanding the interplay between Market Access, Trade Capacity, and population dynamics. Mastering these mechanics allows players to build powerful trade networks that can withstand economic fluctuations and geopolitical challenges.
The system rewards strategic thinking and long-term planning, whether you're establishing your first market center or competing for dominance in shared economic zones. By balancing automation for efficiency with manual control for strategic precision, players can maximize their economic potential while focusing on broader imperial ambitions. As the game continues to evolve with updates like Patch 1.0.8, staying adaptable and responsive to market dynamics will remain essential for economic success in Europa Universalis V.
More Europa-Universalis-V Guides

Europa Universalis V Economy Mastery: Maximizing Ducats, Development & Wealth
Complete guide to mastering EU5's economic system with strategies for tax income, production optimization, trade dominance, and long-term wealth building through population management and strategic development.

Advanced EU5 Colonization Strategy: Build Your Global Empire
Master EU5's sophisticated colonization mechanics with our comprehensive guide to building global empires through strategic range, settler management, and trade optimization.
EU5 Institutions Guide: Mastering Technology Cost & Spread Strategies
Master Europa Universalis V institutions with our complete guide to technology cost penalties, spread mechanics, and the 20% adoption threshold for optimal gameplay.
AI Tactical Companion
Consult with our specialized tactical engine for Europa-Universalis-V to master the meta instantly.